Know All About
TONSILLITTIS
Definition:
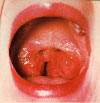
Round marble like collection of lymphoid tissue at the back of the throat, on either side of the food pipe (see picture). Inflammation of the tonsils is tonsillitis. Mind you, just enlargement of tonsils is NOT tonsillitis (Tonsils are small at birth, enlarge during childhood, and become smaller at puberty).
Sex or Age most Affected
Affects all ages, but most common in children between ages 5 and 10.
Signs & Symptons
- Throat pain, either mild or severe
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Chills and fever as high as 1040F (40C) or more
- Swollen lymph glands on either side of the jaw
- Headache
- Ear pain
- Cough (sometimes)
- Vomiting (sometimes)
Causes
Viral or bacterial infection of the tonsils.
Risk Increases With
- Crowded or unsanitary living conditions
- Since tonsillitis is contagious, exposure to a patient.
Prevention
Avoid exposure to people with upper-respiratory infections. Recurrences can be prevented by avoiding self medication and giving antibiotics as advised.
Diagnostic Measures
- Observation of symptoms
- History and exam by a doctor
- Throat culture, in some cases, to differentiate from Diphtheria.
Possible Complications
- Abscess (collection of pus) in the tonsils and adjoining throat, requiring surgical drainage
- Chronic tonsillitis, with recurrent sore throat and greatly enlarged tonsils
- Rheumatic fever, if the bacterial infection is streptococcal and it is not treated with antibiotics, or if antibiotics are discontinued before 10 days
Probable Outcomes
Usually spontaneous recovery. Symptoms generally begin to improve in 2 to 3 days, but treatment MUST be completed.
If attacks of tonsillitis are severe and frequent enough to affect your child’s general health or interfere with schooling, hearing or breathing, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the tonsils. A tonsillectomy involves small risk, but the risk increases with age.
TREATMENT
General Measures
- Give steam inhalation, plain or with Tr Benzoin, to relieve throat irritation and cough.
Medication
- If the tonsillitis is caused by a streptococcal infection, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics for at least 10 days
- To relieve pain, you may use paracetamol.
Activity
- Keep the child away from others until fever and pain disappear
- Normal activity may be resumed when temperature has come to normal.
Diet
Increase all fluid intake. While the throat is very sore, use liquid nourishment, such as milk and soups.
Contact your Doctor
- Your child has fever with throat pain
The following occurs during treatment:
- Symptoms Worsen
- Temperature is normal for 1 or 2 days, then returns
- New symptoms begin, such as: nausea; vomiting; skin rash; thick nasal drainage; chest pain; or shortness of breath
- Convulsion
- Joints become red or painful
- Cough produces coloured (green, yellow, brown or bloody) sputum.
